8550. Print the
chessboard
You are given a chessboard of size n
* n. It is filled with numbers
from 1 to n2 in
the following way: the first ceil(n2 / 2)
numbers from 1 to ceil(n2 / 2)
are written in the cells with an even sum of coordinates from
left to right from top to bottom. The rest of the n2 – ceil(n2 / 2)
numbers from ceil(n2 / 2)
+ 1 to n2 are written
in the cells with an odd sum of coordinates from left to right from top to
bottom.
The operation ceil(x / y) means division x by y rounded up.
Input. One integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 9).
Output. Print the matrix – the chessboard in the given manner. Watch for alignment!
|
Sample input 1 |
Sample output 1 |
|
5 |
1 14 2 15
3 16 4 17
5 18 6 19
7 20 8 21 9 22 10 23 11 24 12 25 13 |
|
|
|
|
Sample input 2 |
Sample output 2 |
|
6 |
1 19 2 20
3 21 22 4 23
5 24 6 7 25
8 26 9 27 28 10 29 11
30 12 13 31 14 32
15 33 34 16 35 17
36 18 |
SOLUTION
array
Algorithm
analysis
Enumerate the rows and columns of the
chessboard from 1 to n. Set the
counter cnt = 1. Iterate
over the cells of the resulting two-dimensional table n * n. Assign the value cnt to each cell with an even
sum of coordinates, and after each assignment, increase cnt by 1. Then iterate through the cells of the resulting table again and
fill the cells with an odd sum of coordinates in the same way.
Example
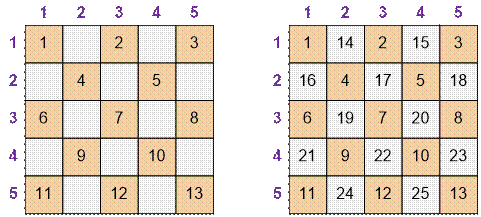
Consider the first example with n = 5.
The first pass through a two-dimensional array is shown on the left, filling the cells with an even sum of
coordinates. The second pass is shown on the right, filling the cells
with an odd sum of coordinates.
Algorithm realization
Declare the two-dimensional array.
#define MAX 110
int m[MAX][MAX];
Read the value of n.
scanf("%d", &n);
The first ceil(n2 / 2) numbers from 1 to ceil(n2 / 2) write to
the cells with even sum of coordinates.
cnt = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if ((i + j) % 2
== 0) m[i][j] = cnt++;
The rest n2 – ceil(n2 / 2)
numbers from ceil(n2 / 2)
+ 1 to n2 write to the cells
with odd sum of coordinates.
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
if ((i + j) % 2
== 1) m[i][j] = cnt++;
Print the two dimensional array.
for (i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j
<= n; j++)
printf("%2d
", m[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}